Ratio Pyrometer : 비율 파이로미터
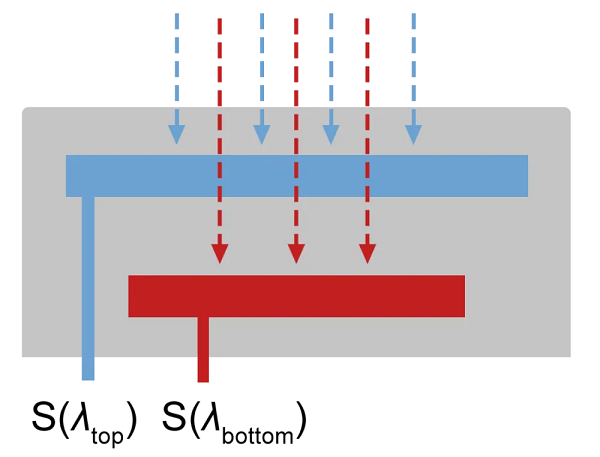
비율 파이로미터는 두 파장 방식을 사용하는 비접촉 온도 측정을 위한 고급 장치입니다. 이 기기들은 종종 이색(two-color), 몫(quotient) 또는 이중 파장(dual-wavelength) 파이로미터라고 불리며, 단색 파이로미터와는 다르게 동작합니다. 단일 파장에서 복사를 측정하는 단색 파이로미터와 달리, 다색 파이로미터는 복사율(emissivity)의 변화나 먼지나 연기와 같은 오염물의 존재와 같은 다양한 조건에서 정확도를 향상시키고 신뢰성을 확보할 수 있습니다.
빈의 변위 법칙(Wien의 변위 법칙)은 흑체가 방출하는 복사의 최대 파장이 온도에 반비례함을 나타냅니다. 물체의 온도가 상승하면 방출되는 복사는 전체 파장 범위에서 증가하고, 스펙트럼 특정 복사의 최대값은 더 짧은 파장으로 이동합니다.
강도 기반의 단일 파장 파이로미터와 비율 기반 파이로미터 사이에는 큰 차이가 있습니다. 단일 파장 파이로미터는 특정 대역폭 내에서 방출된 적외선 복사의 파워를 측정합니다. 반면 비율형 파이로미터는 서로 근접한 두 파장에서 적외선 복사를 측정하여 두 강도 간의 관계를 평가합니다. 이 두 색의 대역폭은 부분적으로 겹칠 수도 있고 완전히 분리될 수도 있습니다. 비율형 파이로미터의 이러한 고유한 접근법은 보다 정확하고 신뢰할 수 있는 온도 측정을 가능하게 합니다.
단일 색 기기와 달리 비율식 파이로미터는 두 파장 신호가 방출율 또는 공정 변화에 의해 비례적으로 영향을 받는 한, 방출율을 알 수 없거나 방출율이 온도에 따라 변하더라도 신뢰성 있게 측정할 수 있습니다. 따라서 이색 파이로미터의 두드러진 특징 중 하나는 열악한 조건에서도 반복 가능하고 정확한 측정을 제공할 수 있다는 점입니다.
Ratio pyrometers는 측정 지점이 물체에 완전히 놓여 있지 않거나 물체가 파이로미터의 스팟 크기보다 작을 때, 또는 파이로미터의 광학 경로에 먼지, 증기, 오염 또는 창문과 같은 전송 변화가 있을 때 자주 사용됩니다. 이러한 장치는 방사율이 알려져 있지 않거나 변하지만 두 파장에서 동일하게 변하는 금속 가공과 같은 까다로운 산업 응용 분야에서 사용됩니다.
대부분의 ratio pyrometers는 반도체 검출기를 사용하여 온도 측정에 대해 1ms에서 20ms의 시간 상수를 가능하게 합니다. 온도 측정 범위의 시작점은 일반적으로 100 °C를 훨씬 웃돕니다.
많은 공급업체는 단일 파장 측정으로 측정된 온도의 병행 표시를 제공합니다. 기울기와
방사율이 올바르게 설정되면, 많은 quotient pyrometers는
차광 또는 창문 오염으로 인한 신호 손실의 퍼센트를 계산하여 표시할 수 있습니다. 고전적인 단일색 파이로미터는
측정 물체의 온도 저하와 광학계 오염을 구별할 수 없지만, ratio pyrometer는 이를 구별할
수 있습니다.
A ratio pyrometer is an advanced device for non-contact temperature measurement using a two-wavelength approach. These instruments, often called two-color, quotient, or dual-wavelength pyrometers, function differently from single-color pyrometers. Unlike single-color pyrometers, which measure radiation at a single wavelength, multi-color pyrometers can improve accuracy and ensure reliability under varying conditions such as changes in emissivity or the presence of contaminants like dust or smoke.
Wien’s displacement law states that the peak wavelength of radiation emitted by a black body is inversely proportional to its temperature. As an object’s temperature rises, its emitted radiation increases across the overall wavelength range, and the maximum of the spectral-specific radiation shifts to shorter wavelengths.
There is a significant difference between intensity-based single-color pyrometers and ratio-based pyrometers. Single-color pyrometers measure the power of the emitted infrared radiation within a specific bandwidth. In contrast, ratio-based pyrometers measure the infrared radiation at two closely spaced wavelengths and evaluate the relationship between the two intensities. The bandwidth of these two colors can be partly overlapping or completely separated. This unique approach of ratio pyrometers allows for more accurate and reliable temperature measurements.
Unlike single-color devices, a ratio pyrometer can measure reliably even when the emissivity is unknown or changing with temperature, as long as both wavelength signals are affected proportionally by emissivity or process changes. Therefore, one of the standout features of the two-color pyrometer is its ability to provide repeatable and accurate measurements even in adverse conditions.
Ratio pyrometers are often used when the measuring spot is not fully placed on the object, the object is smaller than the pyrometer spot size, or when changing transmissions are present in the optical path of the pyrometer—such as dust, steam, dirt, and windows. These devices are utilized in challenging industrial applications, such as metal processing, where emissivity is unknown and changing but alters equally at both wavelengths.
Most ratio pyrometers use semiconductor detectors, allowing for time constants of 1 ms to 20 ms for temperature measurements. The starting point of the temperature measuring range is usually well above 100 °C.
Many suppliers offer a parallel representation of the temperature measured using the single-wavelength measurement. If the slope and emissivity are set correctly, many quotient pyrometers can also calculate and display the percentage signal loss due to shading or window contamination. While a classic single-color pyrometer cannot distinguish between a drop in the temperature of the measurement object and contamination of the optics, a ratio pyrometer has this ability.


