Precision : 정밀도
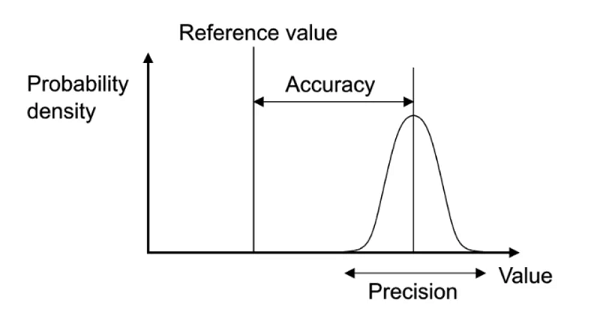
적외선 영상에서의 정밀도는 적외선 장비가 수행한 측정의 일관성과 재현성을 의미합니다. 이는 조건이 변하지 않은 상태에서 반복 측정을 했을 때 측정값들이 서로 얼마나 가까운지를 나타냅니다.
반면 정확도는 측정값이 실제값 또는 측정 대상 물체의 실제 온도에 얼마나 가까운지를 의미합니다. 높은 정확도는 측정이 옳다는 것을 보장하고, 높은 정밀도는 반복 측정이 유사한 결과를 내는 것을 보장합니다.
적외선 측정 장비는 동일한 값(실제값과는 큰 차이가 있는 값)을 일관되게 측정하는 경우 정밀하지만 정확하지 않을 수 있습니다. 반대로 개별 측정값의 변동이 큰 경우 평균적으로 실제값에 근접하면 정확하지만 정밀하지 않을 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 어떤 적외선 센서가 물체의 온도를 측정할 때 실제 온도가 100°C인데 항상 98°C를 읽는다면 정밀하지만 정확하지 않습니다. 다른 센서가 95°C에서 105°C 사이를 읽어 평균이 100°C가 된다면 정확하지만 정밀하지 않습니다.
높은 정밀도를 달성하려면 임의 오차를 최소화하고 측정 시스템의 안정성을 확보해야 합니다. 여기에는 고품질 센서 사용, 안정적인 작동 조건 유지, 강건한 신호 처리 기법 적용 등이 포함됩니다. 정밀도는 일반적으로
측정값의 표준편차나 분산과 같은 통계적 척도로 정량화됩니다.
Precision in infrared imaging refers to the consistency and repeatability of measurements taken by the infrared instrument. It indicates how closely repeated measurements under unchanged conditions are to each other.
In contrast, accuracy refers to how close a measured value is to the true value or the actual temperature of the object being measured. While high accuracy ensures that the measurement is correct, high precision ensures that repeated measurements yield similar results.
An infrared measurement instrument can be precise without being accurate if it consistently measures the same value that is far from the true value. Conversely, an infrared sensor can be accurate without being precise if it hits the true value on average but with significant variation in individual measurements. For example, if an infrared sensor measures the temperature of an object and consistently reads 98°C when the actual temperature is 100°C, it is precise but not accurate. If another sensor reads between 95°C and 105°C, averaging out to 100°C, it is accurate but not precise.
Achieving high precision involves minimizing random errors and ensuring the stability of the measurement system. This includes using high-quality sensors, maintaining stable operating conditions, and employing robust signal processing techniques. Precision is typically quantified by statistical measures such as standard deviation or variance of the measurements.


