Optical Resolution : 광학 해상도
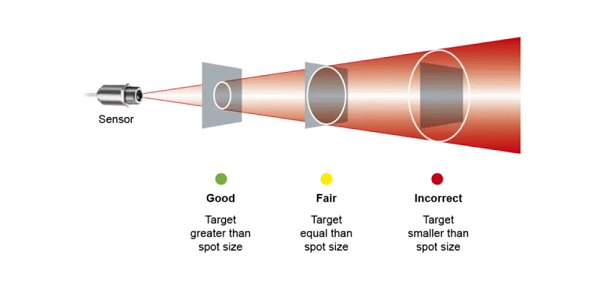
광학 해상도는 온도 측정에 있어 중요한 사양 지표로, 물체를 충분한 정확도로 분해할 수 있는 능력을 나타냅니다. 측정 장비의 시야(FOV)가 작을수록 측정 스폿 크기가 작아지고 대상의 광학 해상도가 높아집니다. 온도 측정 응용에서 높은 광학 해상도는 대상의 모든 필요한 온도 정보를 정확하게 포착하여 효과적인 온도 모니터링과 제어를 가능하게 합니다.
기술적으로 광학 해상도는 측정 장비의 광학 시스템과 관련이 있으며, 광학 온도계(pyrometer)에서는 검출기 크기와, 열화상 카메라에서는 센서의 픽셀 크기와 연관됩니다. 이 둘이 함께 온도 측정 응용에 대한 광학 해상도를 정의합니다.
광학 온도계 응용과 관련하여 광학 해상도는 특정 영역의 온도를 정확하게 측정할 수 있는 능력입니다. 측정 스폿 크기는 광학 온도계의 측정 거리와 함께 변하기 때문에 거리대스폿 비율(D:S 비율)을 사용합니다. 대부분의 경우 스폿 크기가 작고(따라서 D:S 비율이 큰) 것이 유리합니다. 이렇게 하면 광학 온도계가 더 먼 거리에서도 작은 대상들을 감지하여 전문적인 온도 측정을 보장할 수 있습니다. 다만, 정밀한 정렬이 필요하며 이는 종종 레이저나 비디오 조준을 통해 이루어집니다.
대상이 측정 스폿보다 크거나 적어도 동일한 크기인지 확인하는 것이 필수적입니다. 측정 스폿보다 작은 물체를 정확하게 측정할 수 있는 것은 비율형(pyrometer) 광학 온도계뿐이며, 그렇지 않으면 신호가 80% 또는 심지어 90%까지 감쇠하는 부정확성이 발생할 수 있습니다. 정확한 측정을 위해서는 주어진 거리에서 광학 온도계의 측정 스폿 크기를 항상 확인하고 FOV 또는 스폿 크기 계산기 앱을 사용하세요.
열화상 카메라의 경우 광학 해상도는 종종 공간 해상도(spatial resolution)라고도 합니다. 이는 두 개의 점 형태 대상이 서로 분리되어 검출될 수 있는 거리를 나타내며, 레일리 기준(Rayleigh criterion)으로 설명됩니다. 이 기준은 광학계의 F-수와 측정 파장에 따라 달라집니다. 종종 이미징 시스템의 광학 해상도를 설명하기 위해 변조 전달 함수(MTF)가 사용됩니다. 레일리 기준은 MTF가 9%인 상태를 나타내며, 이 값 이하에서는 대상들을 더 이상 구별할 수 없습니다.
열화상 카메라를 이용한 온도 측정 응용에서 광학 해상도는 종종 순간 시야각(IFOV)으로 정의되며, 이는 특정 거리에서 분해할 수 있는 가장 작은 목표물 크기를 나타냅니다. IFOV는 검출기 배열의 단일 픽셀이 생성하는 측정 지점을 의미하고, 전체 시야각(FOV)은 전체 센서 배열을 나타냅니다. 대상체를 최적으로 샘플링하려면 대상체와의 거리를 IFOV의 두 배로 하는 것이 권장됩니다.
열화상 분야에서 고정밀 온도 측정을 위해서는 대상의 크기가 최소한 MFOV와 같아야 합니다. 일반적인 MFOV 값은 3×3 픽셀로 설명되며, 이는 IFOV의 3배에 해당합니다. 자세한 내용은 FOV 계산기를 확인하시기 바랍니다.
Optical resolution is a crucial specification parameter for temperature measurement and indicates the ability to resolve an object with sufficient accuracy. A small FOV (field of view) of a measuring device is associated with a small measuring spot size and a higher optical resolution of the target. In temperature measurement applications, high optical resolution ensures that all necessary temperature information from the target is captured precisely, facilitating effective temperature monitoring and control.
From a technical point of view, optical resolution is linked to the optics system of the measurement device and the detector size for a pyrometer or the sensor’s pixel size for a thermography camera. Both together define the optical resolution for the temperature measurement application.
Related to a pyrometer application, optical resolution is the ability to measure the temperature of a specific area accurately. The measurement spot size varies with the measurement distance of the pyrometer, leading to the use of the distance-to-spot size ratio (D:S ratio). In most cases, it is advantageous to have a small spot size (and therefore a large D:S ratio). The pyrometer can detect small targets even at larger distances and ensure professional temperature measurement. However, precise alignment of the device is required, often realized by laser or video sighting, handling the advanced optical resolution.
It is essential to ensure the object is larger than or at least equal to the measurement spot. Only ratio pyrometers can measure objects smaller than the measuring spot without causing inaccuracies leading to a signal attenuation of 80% or even 90%. To ensure accurate measurement, always check the measurement spot size of a pyrometer at a given distance and use a FOV or spot size calculator app.
For a thermal imaging camera, optical resolution is often referred to as spatial resolution. It indicates the distance at which two point-like objects can be separately detected and thus resolved, described by the Rayleigh criterion. This criterion depends on the F-number of the optics and measurement wavelengths. Often, the Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) is used to describe the optical resolution for imaging systems. The Rayleigh criterion represents a MTF of 9%. Below this value, the objects can no longer be distinguished.
For temperature measurement applications using thermography cameras, optical resolution is often defined by the instantaneous FOV, representing the smallest target size that can be resolved at a specific distance. The IFOV represents the measurement spot generated by a single pixel of the detector array, while the whole FOV represents the full sensor array. For optimal object sampling, an object distance of two times the IFOV is recommended.
For high-accuracy temperature measurement in the field of thermal imaging, the target size should be at least equal to the MFOV. A typical MFOV value is described by 3×3 pixels, which corresponds to 3 times the IFOV. For further details, please check the FOV calculator.


