Diagonal Field of View (DFOV) : 대각 시야각 (DFOV)
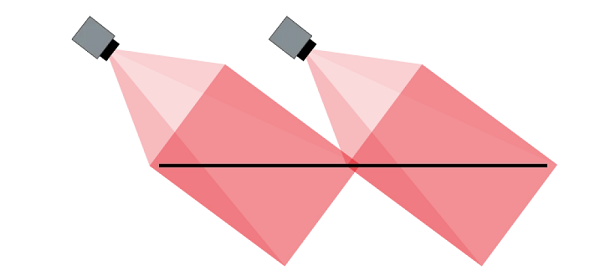
DFOV(Diagonal Field of View, 대각 시야각)는 카메라 시야 내에서 수평 및 수직 방향의 관측 범위를 대각선으로 측정한 전체 각도 범위를 의미합니다. 특정 거리에서 적외선 카메라가 어느 정도의 영역을 촬영할 수 있는지를 아는 것은 매우 중요합니다. DFOV는 카메라의 수평 시야각(HFOV)과 수직 시야각(VFOV)을 이용해 피타고라스 정리를 적용하여 계산할 수 있습니다. DFOV가 클수록 카메라는 더 넓은 영역을 포착할 수 있어, 광범위한 감시나 대규모 장면 모니터링이 필요한 응용 분야에 유리합니다. 반대로 DFOV가 작을수록 보다 작고 세부적인 영역에 집중하는 데 적합합니다. DFOV는 적외선 카메라의 렌즈와 센서 크기에 의해 결정되며, 초점거리가 짧은 렌즈나 큰 센서를 사용할수록 DFOV는 넓어지고, 초점거리가 긴 렌즈나 작은 센서를 사용할수록 DFOV는 좁아집니다.
대각 시야각(DFOV)은 라인 스캐너 응용에서 특히 중요합니다. 적외선 카메라는 종종 라인 스캔 측정을 수행할 수 있는데, 이는 시야의 일부만 활용되면서 이동하는 물체나 표면을 지속적으로 모니터링해야 하는 다양한 산업 응용 분야에서 매우 유용합니다. 라인 스캔 측정은 적외선 카메라가 측정 대상 표면을 가로지르는 하나의 선을 따라 온도 데이터를 획득하는 기법입니다. 측정 대상이 이동함에 따라 이러한 라인 스캔 데이터들이 결합되어 전체 표면에 대한 종합적인 열화상 이미지가 생성됩니다. 이 방식은 컨베이어 벨트, 생산 라인 등과 같이 관심 대상이 지속적으로 이동하는 연속 공정을 모니터링하는 데 매우 효율적입니다. 이 스캔 라인은 전체 시야각을 가로지를 수도 있으며, 임의의 형태를 가질 수도 있습니다. 따라서 DFOV는 해당 적외선 카메라에서 가능한 최대 스캔 라인 폭을 의미합니다.
DFOV는 스캔된 이미지에서 확보할 수 있는 해상도와 세부 표현 수준에 직접적인 영향을 미칩니다. 적절히 최적화된 DFOV는 스캔 영역 전체 폭에 걸쳐 충분한 세부 정보를 제공하도록 스캐너의 성능을 보장합니다. 이러한 시야각과 해상도 간의 균형, 그리고 MFOV를 함께 고려하는 것은 라인 스캐너 응용에서 매우 중요하며, 이를 통해 작은 결함이나 미세한 변화를 놓치지 않을 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, 컨베이어 벨트 위에서 이동하는 금속, 종이, 직물과 같은 대형 시트 소재를 모니터링하는 제조 공정용 라인 스캐너를 생각해볼 수 있습니다. 이 경우 DFOV는 한 번의 스캔으로 소재의 폭 중 어느 정도를 커버할 수 있는지를 결정합니다. DFOV가 너무 좁으면 적외선 카메라가 일부 소재를 놓칠 수 있고, 세부 정보를 충분히 분해해 식별할 수 없게 됩니다. 반대로 DFOV가 적절히 최적화되면 전체 폭을 효율적으로 커버하면서, 결함이나 불균일성을 드러내는 고해상도 열화상 이미지를 안정적으로 획득할 수 있습니다.
DFOV, which stands for Diagonal Field of View, refers to the total angular extent of the observable scene in both the horizontal and vertical directions, measured diagonally across the camera’s field of view. Knowing the coverage area that an infrared camera can capture at a given distance is essential. The DFOV can be calculated using the camera’s horizontal and vertical fields of view (HFOV and VFOV) and applying the Pythagorean theorem. A larger DFOV means the camera can capture a wider area, which benefits applications requiring broad surveillance or monitoring of large scenes. Conversely, a smaller DFOV is useful for focusing on smaller, more detailed areas. The DFOV is influenced by the infrared camera’s lens and the size of the sensor. A lens with a shorter focal length or a larger sensor will result in a wider DFOV, while a longer focal length lens or a smaller sensor will produce a narrower DFOV.
The Diagonal Field of View is particularly important for line scanner applications. Infrared cameras are often capable of performing line scan measurements, which are particularly useful in various industrial applications where continuous monitoring of moving objects or surfaces is required and the field of view is partially occupied. Line scan measurement is a technique where the infrared camera captures temperature data along a single line across the target surface. As the target moves, these line scans are combined to create a comprehensive thermal image of the entire surface. This method is highly efficient for monitoring continuous processes such as conveyor belts, manufacturing lines, or any other application where the object of interest is in constant motion. This line can go across the full field of view and have random shapes. Therefore, the DFOV is the largest scan line width possible for the infrared camera.
The DFOV impacts the resolution and level of detail that can be captured in the scanned image. A well-optimized DFOV ensures that the scanner provides sufficient detail across the entire width of the scanned area. This balance between field of view and resolution, and considering the MFOV, is critical in line scanner applications to ensure that small defects or variations are not missed.
Consider a line scanner used in manufacturing to monitor a large sheet of material, such as metal, paper, or textiles, transported on a conveyor belt. The DFOV determines how much of the sheet’s width can be scanned in one pass. If the DFOV is too narrow, the infrared camera can miss material, and details cannot be resolved. A well-optimized DFOV ensures that the entire width is covered efficiently, capturing high-resolution thermal images that reveal any defects or irregularities.


