Background Radiation : 배경 복사
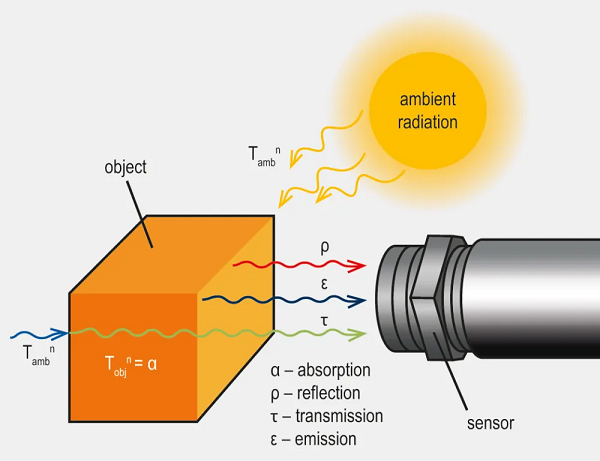
적외선 온도 측정에서 배경 복사(background radiation)란 부분적으로 투명한 측정 대상 물체를 통과해 센서에 도달하는 복사원의 신호 기여분을 의미합니다. 측정 대상의 투과율이 높을수록, 그리고 배경의 온도가 높을수록 배경 복사가 측정 결과에 미치는 영향은 더욱 커집니다.
적외선 온도계는 시야(Field of View) 내에 존재하며 장치가 감광 가능한 파장 범위에 속하는 모든 복사를 감지합니다. 이 복사가 측정 대상 물체 자체에서 방출된 것이든, 측정 대상 물체에 의해 반사된 것이든, 혹은 배경에서 발생하여 측정 대상 물체를 통과해 들어온 것이든 관계없이 모두 검출됩니다. 이 중 후자의 두 가지 복사 성분은 전체 신호에서 차지하는 비중이 측정 대상 물체가 방출한 복사 신호와 비슷하거나 더 클 경우, 측정 대상의 온도 산출을 크게 방해할 수 있습니다. 배경 복사의 수준을 알고 있고 측정 대상 물체의 투과율이 알려져 있다면, 계산을 통해 그 영향을 보정할 수 있습니다. 그러나 일반적으로는 고온의 복사원을 차폐하는 등 기술적인 조치를 통해 간섭 복사가 발생하지 않도록 하는 것이 더 바람직합니다.
In infrared temperature measurement, background radiation refers to the contribution to the sensor signal from a radiation source that radiates through a partially transparent measurement object. The higher the transmittance of the measured object and the higher the temperature of the background, the greater the impact of the background radiation.
An infrared thermometer detects any radiation within its field of view for which it is spectrally sensitive. It doesn’t matter whether this radiation comes from the measurement object, is reflected by the measurement object, or is transmitted through the measurement object from the background. The last two types of radiation can interfere with the temperature determination of the measurement object, especially if their contribution to the overall signal is similar to or greater than the signal of the emitted radiation of the measurement object. If the level of background radiation is known, its influence can be compensated for through calculation, provided that the transmittance of the measurement object is known. However, it is generally better to avoid interfering with radiation by taking technical measures, such as shading hot radiation sources.


