Wien’s Displacement Law : 빈의 변위 법칙
이 관계는 흑체의 복사 모델에서 유도될 수 있으며 플랑크의 복사 법칙에 따르면 오직 그 온도에만 의존합니다.
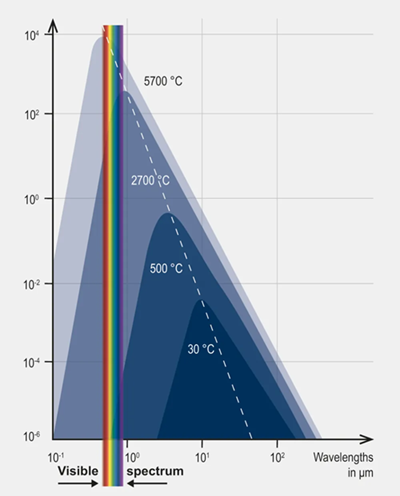
흑체의 열복사는 광범위한 파장 스펙트럼을 형성하는 전자기파로 구성됩니다. 복사의 강도는 플랑크의 복사 법칙에 따라 서로 다른 파장들에 걸쳐 분포합니다. 이 분포는 특정 파장에서 피크를 가지며, 이 피크는 흑체의 온도에 따라 달라집니다. 비엔 법칙에 따르면 흑체의 온도가 상승할수록 이 피크는 짧은 파장 쪽으로 이동합니다. 비엔 법칙은 이 이동의 크기를 계산할 수 있게 해줍니다.
핵심은 흑체의 온도가 높을수록 물체가 최대 복사를 방출하는 파장이 더 짧아진다는 점입니다. 따라서 실온에서는 보이지 않는 적외선만 관찰되지만, 뜨거운 철은 적색에서 암적색을 방출하고, 용융된 철은 백색광 영역에서 방출됩니다.
비엔 변위 법칙은 흑체 복사의 스펙트럼 전력 밀도를 설명하는 플랑크의 복사 법칙에서 유도될 수 있습니다. 비엔 변위 법칙을 유도하려면 플랑크 복사 함수의 피크를 찾아야 합니다. 이는 파장에 대한 함수를 곱의 미분 규칙으로 미분하고 도함수를 0으로 두어 달성됩니다. 수학적 유도 과정을 거치면 최대 복사 강도가 위치하는 파장을 설명하는 비엔 법칙의 공식이 도출됩니다.
Wien’s displacement law states that the wavelength at which a black body emits its maximum radiation is inversely proportional to its absolute temperature T. This means that if the temperature of the emitter doubles, the wavelength of the peak radiation is halved. For instance, the color of a glowing object changes from reddish at 1000 K to whitish at 3000 K and to bluish at 10000 K, as the temperature increases and the peak wavelength becomes shorter.
This relationship can be derived from the radiation model of a black body and depends solely on its temperature, according to Planck’s radiation law.
The thermal radiation of a black body consists of electromagnetic waves that form a broad spectrum of wavelengths. The intensity of the radiation is distributed across different wavelengths according to Planck’s radiation law. This distribution is characterized by a peak at a certain wavelength, which depends on the temperature of the black body. According to Wien’s law, this peak shifts towards shorter wavelengths as the temperature of the black body increases. Wien’s law allows us to calculate the magnitude of this shift.
The key point is that the higher the temperature of the black body, the shorter the wavelength at which the object emits its maximum radiation. Therefore, at room temperature, we find only invisible infrared rays, while hot iron emits red to dark red rays, and molten iron emits in the white light range.
Wien’s displacement law can be derived from Planck’s radiation law, which describes the spectral power density of the radiation of a black body. To derive Wien’s displacement law, one must locate the peak of Planck’s radiation function. This is achieved by differentiating the function for the wavelength using the product rule and setting the derivative to zero. After mathematical derivation, the formula of Wien’s law is obtained, which describes the wavelength at which the maximum radiation intensity lies.
λmax=2897,8μmKT


