Wedge Effect : 웨지 효과
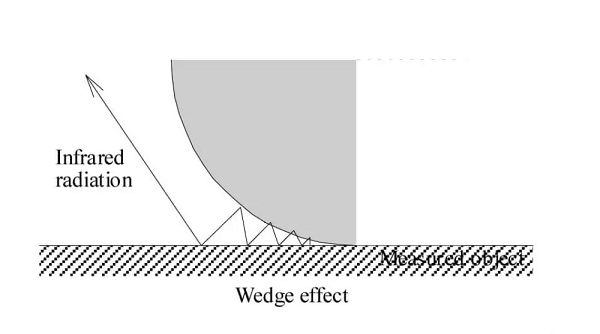
웨지 효과는 적외선 열화상에서 홈, 틈, 음영 등 쐐기 모양 구조 내부에 표면이 있을 때, 평평할 때보다 표면의 겉보기 방사율(apparent emissivity)이 증가하는 현상을 설명합니다. 이러한 방사율 증가는 쐐기 내부에서 적외선 복사가 여러 번 반사되기 때문에 발생합니다. 복사가 쐐기 내에서 반사될수록 각 반사는 복사가 흡수되고 재방출될 확률을 높여 표면의 겉보기 방사율을 증가시킵니다.
이 내부 반사들의 결합된 효과는 물질의 고유 방사율과 무관하게 방사율 값이 거의 흑체 조건에 근접하는 결과를 낳아, 방사율이 약 0.998에 도달할 수 있습니다. 이 효과는 물질 방사율의 차이나 외부 복사의 영향을 온도 측정 정확도에 미치는 영향을 최소화합니다. 이러한 높은 방사율을 얻으려면 쐐기의 깊이가 개구부보다 훨씬 커야 합니다.
웨지 또는 반웨지 효과를 적용하면 홈이나 틈과 같은 자연적 또는 인공적 쐐기가 존재할 때 표면의 방사율을 높이는 데 효과적입니다.
The wedge effect describes in infrared thermography the increase in apparent emissivity of a surface when it resides within a wedge-shaped structure, such as a groove, slit, or recess, compared to when it is flat. This heightened emissivity occurs due to multiple reflections of infrared radiation inside the wedge. As radiation bounces within the wedge, each reflection enhances the probability of the radiation being absorbed and re-emitted, thereby increasing the surface’s apparent emissivity.
The combined effect of these internal reflections results in a near-blackbody condition, with emissivity values nearing 0.998, independent of the material’s intrinsic emissivity. This effect minimizes the influence of variations in material emissivity or external radiation on the accuracy of temperature measurements. Achieving such high emissivity requires the wedge’s depth to be considerably larger than its opening.
Applying the wedge or semi-wedge effect boosts the emissivity of surfaces, effective when natural or artificial wedges, such as grooves or slits, are present.


