Ambient Temperature : 주변 온도
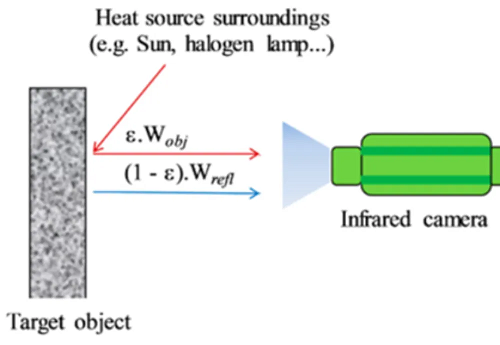
주변 온도(Ambient temperature)란 측정 대상 물체 또는 고온계(파이로미터)·적외선 카메라를 둘러싼 환경의 온도를 의미합니다. 이 온도는 적외선 온도 측정에 두 가지 주요한 방식으로 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 첫째, 주변 온도는 장치의 내부 온도에 영향을 주며, 이는 다시 검출기의 감도 변화로 이어질 수 있습니다. 특히 검출기가 주변 환경에 직접 노출되어 있고 충분히 단열되어 있지 않은 경우 그 영향은 더욱 커집니다. 일반적으로 장치의 펌웨어는 주변 온도가 측정 온도 값에 미치는 영향을 보정하는 기능(온도 계수 보정)을 포함하고 있지만, 적외선 온도계는 반드시 제조사가 규정한 주변 온도 범위 내에서 사용해야 합니다.
둘째, 측정 대상 물체의 방사율이 1.000보다 낮고, 물체 자체의 온도 복사에 비해 물체에서 반사되거나 물체를 통과한 주변 복사가 전체 검출 복사 에너지에서 차지하는 비중이 클 경우, 주변 온도는 측정 결과에 직접적인 영향을 미칩니다. 이러한 복사 성분을 고려하고 방사율이 1이 아닌 경우를 보정하기 위해 보정 계산이 수행됩니다. 이때 장치 설정에서 주변 온도 입력값의 출처를 올바르게 선택하는 것이 매우 중요합니다. 기본적으로는 적외선 측정 장치의 내부 온도를 주변 온도의 근사값으로 가정하며, 이는 많은 측정 상황에서 충분히 적합합니다. 그러나 측정 대상의 주변 온도가 장치 온도와 크게 다른 경우(예: 오븐 내부의 물체를 관측창을 통해 측정하는 경우)에는 실제 주변 온도를 설정 메뉴에서 수동으로 입력하거나 통신 인터페이스를 통해 별도로 입력해야 합니다.
경우에 따라서는 두 가지 서로 다른 주변 온도를 고려해야 할 수도 있는데, 이는 부분적으로 투명한 물체를 측정할 때 물체의 앞쪽과 뒤쪽 환경 온도가 서로 다른 경우가 이에 해당합니다. 또한 복사 히터나 가스 화염과 같은 강한 인공 복사원이 측정에 영향을 미치는 상황에서는, 이러한 복사원이 흑체 복사체가 아니며 파장에 따라 서로 다른 방사율 특성을 가진다는 점을 고려해야 합니다. 따라서 이러한 복사원이 존재하는 환경에서 온도를 측정할 때에는 사용되는 적외선 온도계의 종류와 해당 장치가 감지할 수 있는 파장 범위를 함께 고려하는 것이 중요합니다.
Ambient temperature refers to the temperature surrounding the object being measured or the pyrometer/infrared camera. This temperature can affect infrared temperature measurement in two main ways. Firstly, it can influence the internal temperature of the device, which in turn affects the sensitivity of the detector, especially if the detector is also exposed to the ambient temperature and is not adequately insulated. The device’s firmware usually compensates for the influence of ambient temperature on the measured temperature value (referred to as the temperature coefficient), but it’s important to operate the infrared thermometer within its specified ambient temperature range.
Secondly, ambient temperature affects the measurement result when the object being measured has an emissivity of less than 1.000 and when ambient radiation reflected by or transmitted through the object significantly contributes to the overall radiation detected, compared to the temperature radiation of the object itself. Corrections are made to account for these radiation contributions and to compensate for an emissivity different from 1. It’s crucial to select the correct source for the ambient temperature in the device’s configuration. By default, the internal temperature of the infrared measuring device is assumed as an approximation for the ambient temperature, which is suitable for many scenarios. However, if the object’s ambient temperature significantly differs from the device’s temperature (e.g., in the case of measuring an object inside an oven through a viewing window), the actual ambient temperature needs to be set manually in the configuration or input via a communication interface.
In some cases, two different ambient temperatures must be considered, such as when measuring a partially transparent object where the ambient temperature in front of and behind the object differs. Additionally, when considering the influence of intense artificial radiation sources like radiant heaters or gas flames, it’s important to note that these sources are not blackbody radiators and have varying emissivity across different wavelengths. This means that the type of infrared thermometer used and the wavelengths it can detect should be considered when measuring temperature in the presence of these radiation sources.


