Thermal Detector : 열형 검출기
양자 검출기 외에 열형 검출기는 적외선 검출기의 두 번째 유형입니다. 이들은 전자기 복사의 흡수로 인해 요소의 온도 변화에 기반합니다. 온도 변화는 열형 검출기의 온도 의존적 성질의 변화를 초래하며, 이는 전기적으로 평가되어 흡수된 에너지의 척도가 됩니다. 이 개념에는 다양한 기술적 구현 방식이 있습니다:
두 서로 다른 금속의 접합부가 가열되면 열전 효과로 인해 온도에 비례하는 전압이 발생합니다. 이 효과는 오랜 기간 동안 열전쌍(thermocouple)을 사용한 접촉식 온도 측정에 활용되어 왔습니다. 만약 접합부의 가열이 복사의 흡수로 인해 발생한다면, 이 구성요소를 서모파일(thermopile)이라고 합니다.
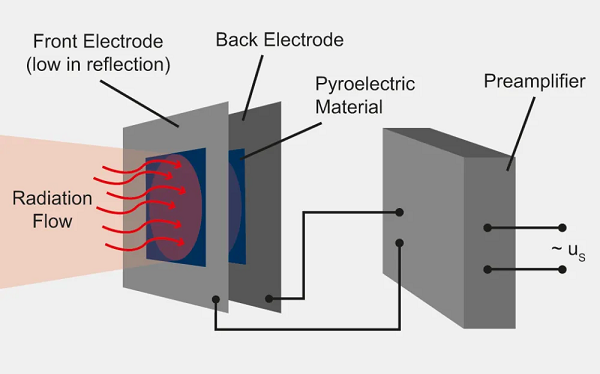
파이로전기 검출기의 경우, 민감한 요소는 증착(evaporation deposition)으로 부착된 두 전극을 가진 파이로전기 물질로 구성됩니다. 적외선 흡수로 인해 검출기 요소의 온도 변화는 파이로전기 효과로 인해 표면 전하의 변화를 초래합니다. 이는 전기적 출력 신호를 생성하며 추가로 처리됩니다. 파이로전기 물질에서 전하가 생성되는 방식 때문에 복사 흐름은 교대로 연속적으로 차단(chopping)되어야 합니다. 그렇지 않으면 이러한 검출기는 온도 변화(예: 모션 센서) 감지에 적합합니다.
볼로미터(bolometer)는 전기 저항의 온도 의존성에 기초합니다. 민감한 검출 요소는 저항기로 구성되며, 열 복사가 흡수되면 그 값이
변합니다. 저항 변화는 볼로미터 저항에 걸리는 신호 전압 강하의 변화를 초래합니다.
In addition to quantum detectors, thermal detectors are a second type of infrared detector. They are based on a temperature change of the element through the absorption of electromagnetic radiation. The change in temperature causes a change in a temperature-dependent property of the thermal detector, which is evaluated electrically and is a measure of the absorbed energy. There are different technological implementations of this concept:
When the junction of two different metals is heated, an electrical voltage proportional to the temperature is produced due to the thermoelectric effect. This effect has been utilized for many years for technical contact temperature measurements using thermoelements. If the heating of the junction is caused by the absorption of radiation, then this component is known as a thermopile.
For pyroelectric detectors, the sensitive element consists of a pyroelectric material with two electrodes attached by evaporation deposition. The temperature change in the detector element created by the absorption of infrared radiation causes a change in surface charge as a result of the pyroelectric effect. This results in an electrical output signal which is processed further. Due to the way that charge is created in the pyroelectric material, the radiation flow must be continuously interrupted in an alternating manner (chopping). Otherwise, such a detector is well suited for detecting temperature changes (e.g., in motion detectors).
The bolometer is based on the temperature dependence of electrical resistance. The sensitive detector element comprises a resistor, whose value changes when heat radiation is absorbed. The change in resistance causes a change in the signal voltage drop across the bolometer resistance.


