Spot : 스팟
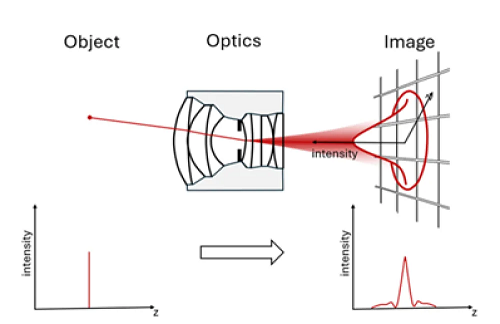
스팟(spot)은 초점점이라는 기하학적 개념의 한계를 극복하기 위한 보다 현실적인 개념입니다. 완벽한 점 형태의 분포 대신에 에어리 디스크(Airy-disc) 또는 에어리 패턴(Airy-pattern)이라고 불리는 더 큰 스팟이 얻어집니다. 이것은 원형 조리개를 가진 광학 시스템이 빛을 초점화할 수 있는 가장 작은 스팟입니다. 센서 위에 에어리 디스크 분포를 생성하는 것은 영상 시스템의 최선의 경우이며, 이는 수차 없이 동작하고 빛의 회절에 의해서만 제한되는 광학 시스템을 설명합니다.
빛이 원형 조리개를 통과할 때 중심에서 바깥으로 강도가 감소하는 동심원의 고리로 특징지어지는 에어리 디스크를 형성합니다. 대부분의 에너지는 잘 중심화되어 있으며 첫 번째 영점(zero point) 내부에 국한되어 있고, 이는 다음과 같이 주어집니다: r0=1.22∙λ∙N
여기서 λ는 적용된 파장이고 N은 광학계의 F-수(F-number)입니다. 첫 번째 영점까지 포획된 에너지는 84%입니다. 이는 스팟 지름이 다음과 같음을 의미합니다: d=2.44∙λ∙N
공식에서 보이듯이, 에어리 디스크의 직경은 사용된 측정 파장에 크게 의존합니다. 열화상 응용에서는 일반적으로 8–14 µm의 파장대가 사용됩니다. 이는 열화상 측정에서 시각 영상 응용보다 더 큰 스폿 크기를 의미합니다. 검출기가 그 특유의 스펙트럼 응답 파장을 가지도록 선택되면 회절 분포의 크기는 오직 F-숫자(F-number)만으로 제어될 수 있습니다.
스폿 크기는 광학 해상도와 밀접하게 연결되어 있습니다. 회절한계(diffration-limited)의 광학 시스템으로 두 점을 해상하는 것은 그들의 에어리 패턴(Airy 패턴)에 달려 있으며, 그 패턴들은 적어도 다음의 거리만큼 떨어져 있어야 합니다 : r0
변조 전달 함수(Modulation Transfer Function, MTF)는 서로 다른 대상 크기와 거리에서의 콘트라스트를 비교하여 이를 정량화합니다. 두 점 사이에서 MTF가 9%를 넘는 시스템은 두 점을 해상한 것으로 간주됩니다. 실무에서는 IFOV(Instantaneous Field of View)의 설명을 사용할 수 있는데, 해당 크기의 물체들은 적절한 광학 해상도를 얻기 위해 IFOV의 두 배 거리를 가져야 합니다. 이는 두 물체의 영상을 샘플링할 때 두 스폿 사이에 비조명(어두운) 픽셀이 항상 필요함을 의미합니다.
에어리 디스크(Airy disk)를 생성하는 광학계를 회절 한계(diffraction-limited) 시스템이라고 합니다. 파장대와 F-값이 고정되어 있을 때 도달할 수 있는 최상의 성능입니다. 실제로는 광학계의 수차와 광학-기계적 공차가 고려되어야 하며, 이는 센서에 맺히는 영상 분포에 큰 영향을 미칩니다. 정량적으로는 Karl Strehl의 이름을 딴 스트렐 비(Strehl Ratio, SR)로 나타냅니다. 이는 실제 스폿 또는 수차가 있는 패턴의 강도를 이상적인 에어리 디스크와 비교한 값입니다. SR이 0.8보다 크면 시스템이 거의 회절 한계에 도달한 것으로 간주되며, 0.8보다 작으면 수차의 영향이 상당함을 시사합니다.
현미경이나 리소그래피처럼 극히 높은 광학 해상도를 요구하는 응용에서는 에어리 디스크 직경을 줄이고 세부 가시성을 향상시키기 위해 더 짧은 파장을 사용합니다. 적외선 카메라를 사용하는 열화상(thermography) 응용에서는 파장대가 보통 실온(T=300 K)에서 물체를 측정할 때 8–14µm입니다. 이러한 거동은 플랑크 법칙(Planck’s law)에 의해 기술되며 흑체의 방출 스펙트럼을 특징지웁니다. 경쟁력 있는 NETD를 가진 적외선 카메라로 저온을 측정하는 것은 종종 장파 적외선(LWIR)에 한정됩니다. 이러한 이유를 인식할 때, 에어리 디스크 직경을 개선하는 유일한 방법은 목표물의 높은 광학 해상도를 얻기 위한 고급 열화상 광학입니다.
A spot is a more realistic concept to overcome the geometric notion of the focal point. Instead of a perfect point-like distribution, larger spots are obtained, which are referred to as Airy-discs or Airy-patterns. This is the smallest spot in which light can be focused by an optical system with a circular aperture. The generating of an Airy disk distribution on the sensor is the best case of the imaging system and describes an optical system operating without aberration and is limited only by the diffraction of light.
As light passes through the circular aperture it forms an Airy disk characterized by concentric rings with decreasing intensity from the center outwards. Most of the energy is well centered and is localized inside the first zero point, it is given by: r0=1.22∙λ∙N
where λ is the applied wavelength and N is the F-number of the optics. The encircled energy up to the first zero is 84%. This leads to the diameter of spot size: d=2.44∙λ∙N
As the formula shows, the diameter of the Airy disk strongly depends on the used measurement wavelength. For thermal imaging application the waveband of 8-14 µm is commonly used. That indicates for thermography larger spot sizes compared visual imaging applications. If the detector with its typical spectral response wavelength is chosen, only the F-number can control the size of the diffraction distribution.
The spot size is strongly connected to the optical resolution. Resolving two points by a diffraction-limited optical system depends on their Airy pattern which must have at least the distance of r0
The Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) quantifies this by comparing the contrast at different target sizes and distances. A system achieving a MTF greater than 9% between two points is considered to have resolved them. For practical application one can use the description of the IFOV where objects of that size must have a distance of two times the IFOV to gain a suitable optical resolution. That means for sampling the image of the two objects an unilluminated pixel between the two spots is always necessary.
An optical system which is generating an Airy disk is called a diffraction-limited system. This is the best performance reachable if waveband and F-number are fixed. In practice, aberration of the optics and opto-mechanical tolerances must be considered and are influencing the imaged distribution on the sensor strongly. Quantitatively it is given as the Strehl Ratio (SR), named after Karl Strehl. It compares the intensity of the real spot or aberrated pattern with the ideal Airy disk. A SR greater than 0.8 indicates a system is nearly diffraction-limited, while less than 0.8 suggests significant aberration impacts.
In applications requiring extremely high optical resolution, such as microscopy or lithography, shorter wavelengths are used to reduce the Airy disk diameter and enhance detail visibility. For thermography application using an infrared camera the waveband is usually 8-14µm especially for measuring objects at room temperature (T=300 K). That behavior is described by Planck’s law characterize emission spectrum of a blackbody. Measuring low temperatures with a competitive NETD of the infrared camera is often limited to the LWIR. Recognize this reason, the only way to improve Airy disk diameter is an advanced thermal imaging optics to gain a high optical resolution of the target.


